Melatonin is one of the most popular sleep aids in the world, widely used by people who struggle with falling asleep or maintaining a consistent sleep schedule. While many think of melatonin as a simple supplement, it’s actually a natural hormone your body already produces every evening. Understanding how melatonin works, when to use it, and how to get the most benefit from it can transform your nighttime routine and help you sleep more deeply.
Your brain produces melatonin in response to darkness. When the sun sets or lights dim, your pineal gland releases melatonin, signaling that it’s time to slow down and prepare for rest. But in modern life, screens, bright lights, irregular schedules, and stress can all interfere with this natural rhythm, leading to delayed sleep and restless nights. Supplementing with melatonin can help reset your internal clock and restore your natural sleep cycle.
One of the biggest benefits of melatonin is its ability to help people fall asleep faster, especially when insomnia is caused by stress, jet lag, shift work, or lifestyle habits. Unlike prescription sleeping pills, melatonin doesn’t force your body into sleep — it gently guides your brain toward a relaxed, sleep-ready state. This makes it a favorite for people who want a natural option that supports, rather than overrides, their body’s rhythms.
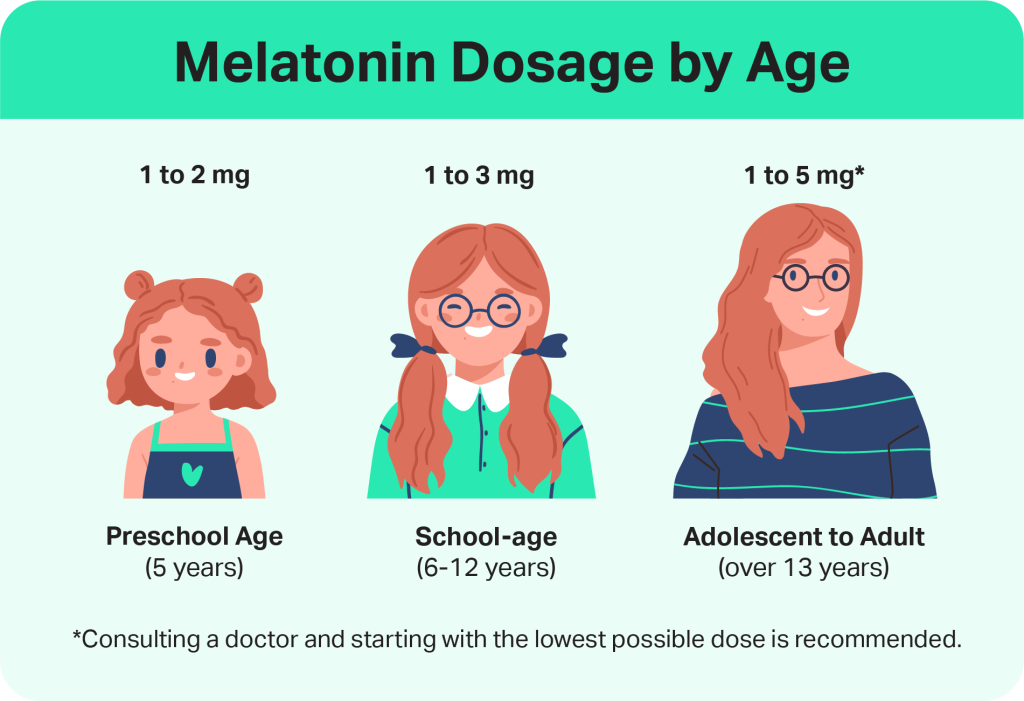
When taking melatonin, timing is everything. Melatonin works best when taken 30 to 90 minutes before bedtime, giving your body enough time to absorb it and respond. Taking it too late can make you groggy the next morning, while taking it too early can confuse your internal clock. Dosage also matters — for most adults, low doses are often more effective than large ones. Small amounts mimic your natural nighttime rise in melatonin and support smoother, more natural sleep.
Melatonin also plays an important role in regulating your circadian rhythm — the internal 24-hour clock that manages sleep, energy, and hormone cycles. When your circadian rhythm is disrupted, everything from mood to focus to digestion can be affected. Using melatonin for a short period can help restore balance, especially if you’re experiencing a major schedule change or sleep disruption.
However, melatonin isn’t a magic fix. It works best when paired with good sleep hygiene: dimming lights at night, reducing screen exposure, maintaining a consistent bedtime, and creating a calm sleep environment. Melatonin can start the process, but your habits complete it.
Most people tolerate melatonin well, though some may experience mild effects like vivid dreams, next-day grogginess, or headaches. These are typically linked to high doses or poor timing. Starting with a small amount and adjusting gradually can minimize discomfort while maximizing benefits.
Melatonin is a powerful tool when used correctly — a natural way to support deeper, more consistent sleep without relying on harsh chemicals. By understanding how it works and using it thoughtfully, you can transform your sleep routine and wake up feeling more energized, balanced, and ready for your day.




